
Micro-service architecture provides a range of technical benefits that contribute to the development velocity and product quality in software projects, while also contributing to the overall business agility
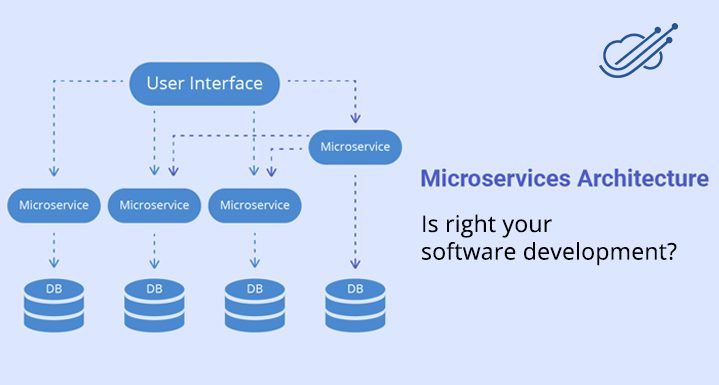
Microservices has been gaining grounds in the software development since the term came into the existence. Microservices aka Microservice architecture is the variant of service-oriented architecture (SOA) for developing large applications where services are grained into chunks as per business domain. It provides continuous delivery/deployment of complex applications and makes the application easier to understand, develop, test and is more resilient to the architecture erosion. The microservice architecture provides a new way to weave existing system in novel ways in order to deliver software solutions quickly.

- Presentation Layer — It is the topmost layer of the application and describes the user interface. The main function is to translate tasks and results to something that the user can understand. User interface code is written in the client-side technologies like HTML, JavaScript, and CSS.
- Business Layer — This layer makes logical decisions and performs calculations. It processes the data between two layers and uses technologies like Spring.
- Data Access Layer — Here the information is stored and retrieved from the database. The information is passed to the business layer and then ultimately to the user. It uses ORM tools like Hibernate to process the info
Here, web application client sends a request; the tier executes the business logic, the database stores the application specific data and the UI displays the specific data to the user. But, as they share the same code base, several problems are likely to occur.
This type of architecture worked well for some duration, but due to the increasing need for continuous delivery, there are multiple issues with this model.
- Operational Overhead: Different stakeholders work with the different layer of monolithic application; hence the team will be confined to the specific domain expertise. The team who works on the presentation layer are specialized in UI technologies but have the least knowledge of data access layer. Hence, if a new feature is to be added, it requires different teams to coordinate and deliver a particular feature. This results in more time-span from ideation to time-to-market and ultimately affects the business ROI.
- Software stack autonomy: It limits technology choices and forces an entire layer to use the single framework. For instance, if the presentation layer is written in an HTML framework, the whole layer is to be implemented within the same framework. This refrains from implementing the latest technology, which results in the application code on becoming obsolete in a short time..
- Implicit Interface: As this codes are released in the single file, a minor change in the application calls for the rebuilding of the entire application. Due to this, on-going applications are put down and results in the need of redeploying the new version. This nature results in fewer updates and is not able to evolve as fast as they should.
- Scalability: Monolithic applications possess one-dimensional scalability; hence fails to scale the individual components. So, the entire application needs to be scaled even though most of the applications might not require scaling.
Developing software without a good architecture can incur much of the cost to the organization. For instance: if a software development company developed a software by following a non-modular approach where UI functionalities and business functionalities are mixed in the same sourced files, the company may need to invest much to support their application in the latest smart-phone native apps. This badly affects software maintainability and increase the time-to-market which ultimately affects the sales of the company.
Monolithic architectures have been the traditional approach, but limitations with scaling, difficulties in maintaining a large codebase, high-risk upgrades, and large upfront setup costs have compelled enterprises or Software Development Company to explore different approaches. Monolithic applications are a tough nut to crack and are difficult to understand and scale with time.
So, to avoid such problems, Microservice Architecture can be a savior! It provides the 360-degree twist to solve the above-mentioned complexities; helping software development companies to stand tall amongst competitors.
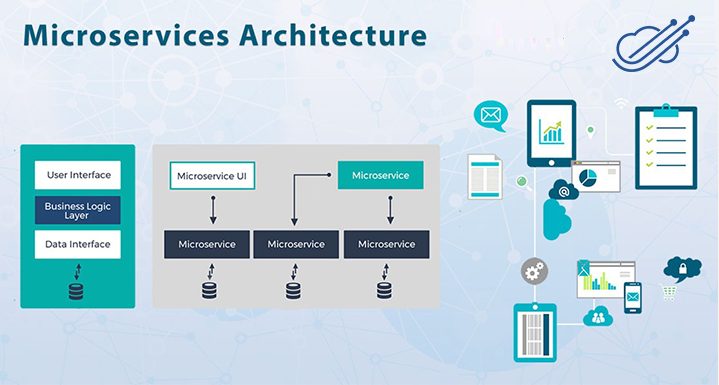
Microservice is the software development technique which structures an application as a collection of loosely coupled service. Each service is self-contained and should implement a single business capability. Microservice architecture is designed to overcome the challenges, failure, and breakdown of the larger applications. Microservices provides opportunities to add resiliency to the system so that components can handle spikes and errors gracefully. With this, every stakeholder can focus solely on one particular element of an overall application, with their own programming style without concerns about other components. The communication in micro-services can be carried out effortlessly because they are stateless and in the well-defined interface (request and response are independent).
If applications/software are developed using microservices methodologies, it will help to adopt DevOps approaches and would eliminate the deployment inefficiencies which would result in less time-to-market. As microservices are device-and platform-agnostic, it enables to develop the applications that provide enhanced user-experience across most of the platforms including web, mobile, IoT, tablets, wearables and many more.
For instance: Walmart Canada used monolithic architecture before 2012! The company faced glitches in handling 6 million page views/minutes which consumed more time and resulted in fewer sales. Due to such issues, they refactored their software architecture to microservices and found the instant result and high conversion rate overnight. Downtime was minimized and the company was able to use cheaper x86 servers rather than expensive hardware commodity which resulted in cost savings between 20%-50%.
It is the natural evolution of SOA in which various technology stacks bring technology diversity into the development team. Both SOA and Microservices allow complex workload to be broken down into smaller, more manageable and independent pieces.
However, there are some basic differences between both of them.
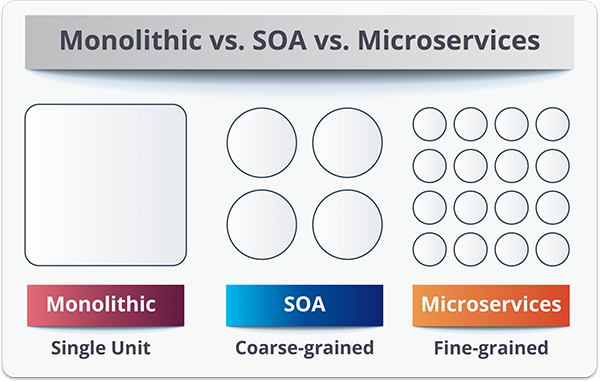
Microservices
- Focuses on decoupling and bounded context
- Systematic change creates new service
- Focuses on continuous delivery and Devops
- Uses the simple messaging system for communication
- Use lightweight protocol such as HTTP , Rest , etc
- Provides independent data storage
SOA
- Goals to maximize re-usability
- Systematic change calls for modifying monolithic architecture
- Do continuous delivery and Devops but it is not mainstream
- Use of Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) for communication
- Supports message protocol
- Shared data storage
The philosophy of microservice is similar to the Unix philosophy i.e. “Do one thing and do it well”. Characteristics are described as below…
- Componentization to perform the single functionality
- Organized as per business capabilities
- Focuses on products not process
- Decentralized governance and data management
- Service is elastic, resilient, composable, minimal and complete
- Improved Productivity and Speed
With microservice, productivity and speed can be easily tackled. The different team works on different components simultaneously without having to wait for one team to finish the task. This results in speeding up the quality assurance as each micro-service can be tested individually. Other stakeholders can work on enhancing the components that are already developed, while other programmers are working on other ones. This increases the speed and leads to the faster release of the product.
- Aligned with the organization
If an organization is using micro-service, team size can be defined to match with the required tasks. Moreover, teams can be broken down into smaller groups and can focus on single components of the application. As the end goal is customer satisfaction and great user experience, the team is not divided into UI team, database team and so on. For instance, if a team working in UAE is handling three services while the team working in California is handling five services, each team working in California and UAE can release and deploy different functionalities independently. These cross-functional teams work towards the fulfillment of one single functionality breaking down the silos between team fostering better collaboration.
- Provides scalability
Microservices scale the parts that have performance issues and use the hardware that best matches service requirements. As each service is the separate component, scaling can be deployed using more containers, enabling more effective capacity planning, less licensing cost and appropriate hardware. Components of the critical service can be deployed on the multiple servers for the increased availability and performance without impacting the performance of the other service. This scalability results in better customer-experience and increases cost-savings.
- Easy to modify technology stack
With microservices, a software development company can try new stack or the latest technologies on the specific components to increase usability and avail larger benefits at the application level. As there are no dependency issues, software developers can avoid using particular technology stacks if they are not providing consistent user-experience. With such continuous modernization, your system won’t become easily outdated.
- Improves fault-isolation
In Microservice architecture, developers are aware of exactly on where to look for the issues to get solved. If a single module is affected, it can be easily demolished or resolved without other parts of an applications getting affected; increasing application’s availability. This is exactly contradictory in the monolithic application; failure of a single component can pull down entire application. For instance, mobile gaming applications (built on monolithic architecture) which have different components like payment, login, player, history, and others. If a particular component, starts to consume more memory space, the entire application will be affected which would result in a poor user experience.
Just because, everything looks flowery, it doesn’t mean it is perfect for the software industry; it does have potential pains which also need to be addressed:-
- Testing of microservice based application can be a painful task because each dependent service needs to be confirmed before starting the testing. As the number of services increases, complexities don’t remain at the backstage! Keeping tabs on all services becomes impractical because, there may occur database errors, network latency, caching issues etc. Hence, resiliency testing and fault injection become a must.
- As microservice focuses on distributed systems and independent service each request needs to be handled carefully between the modules. It may happen that one of the services doesn’t respond which forces developers to write the extra code to avoid disruption.
- Each service depends on its own API and platform, tracking down everything can be a pain-stacking job. A leader needs to monitor multiple entities and manage the entire infrastructure because if in-case any service fails, it becomes tedious to track down the issues. Thus, robust monitoring becomes necessary.
With the continuous delivery and rapid development, employees must pace up with the agility and speed requires availing the benefits from micro-services. If they take a long span of time to provision a server, the company can be in a serious trouble.
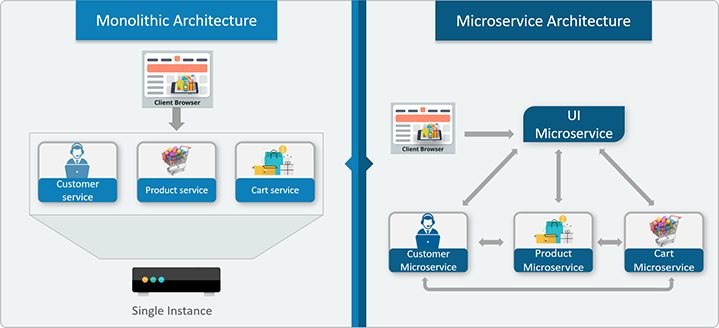
Microservices Architecture
- Each components in the entire application must be small and must deliver and end-goals
- Services are fast
- Even if one service goes down, it doesn’t affect other components. Other services are carried on
- Loosely coupled and decentralized. All works independently.
- More resources can be used for generating high revenue
- Application scaling is possible, hence hardware can be allocated as per the requirements
- Microservices are rapidly developed and continuously available
- Communicates with other micro-services by a well defined interfaces.
- Focus on product
- Different technologies can be used for different micro-service
Monolithic Architecture
- Follows single tier architecture for all business goals
- Takes more time
- If there is an issue in one specific feature, the whole system needs to be pulled down
- All services are tightly coupled
- More resource allocation is not possible as services are not isolated
- Scaling is a bit difficult: hence hardware allocation can be wasteful
- A process needs to start from the scratch; rapid development becomes difficult.
- Communication can be messed up
- Focuses on entire project
- Latest technologies cannot be used as one program depends on others
You might have got the clear scenario about Microservice architecture and the potentiality it possesses to change the software industry! With the increasing use of the digital technologies and multiple device support; software development is diving down into the complex process. But the software industry is blessed with the Microservice architecture which can serve as the perfect solution to solve complexities for software development companies. If companies think to adopt it, it would surely affect the culture technically and operationally.
Today, with the rise in the micro-service, most of the organizations are pulling down monolithic architecture and adopting modern one to leverage in the cut-throat competition. Some of them include Netflix, eBay, Amazon, Twitter, PayPal, Walmart and many more…
